Introduction to Cloud Foundations Spring Semester
Class Notes April 8th - June 21
Top Links for Spring
| Slack Channel for communication | SkillBuilder Link for E-Learning | Pete's Ai "Ask a Question" | 1:1 Office Hours on Demand |
|---|---|---|---|
| Click Here for Slack | Click here for E-Learning | Click here for Ai Q&A | Click Here for 1:1 Office Hours |
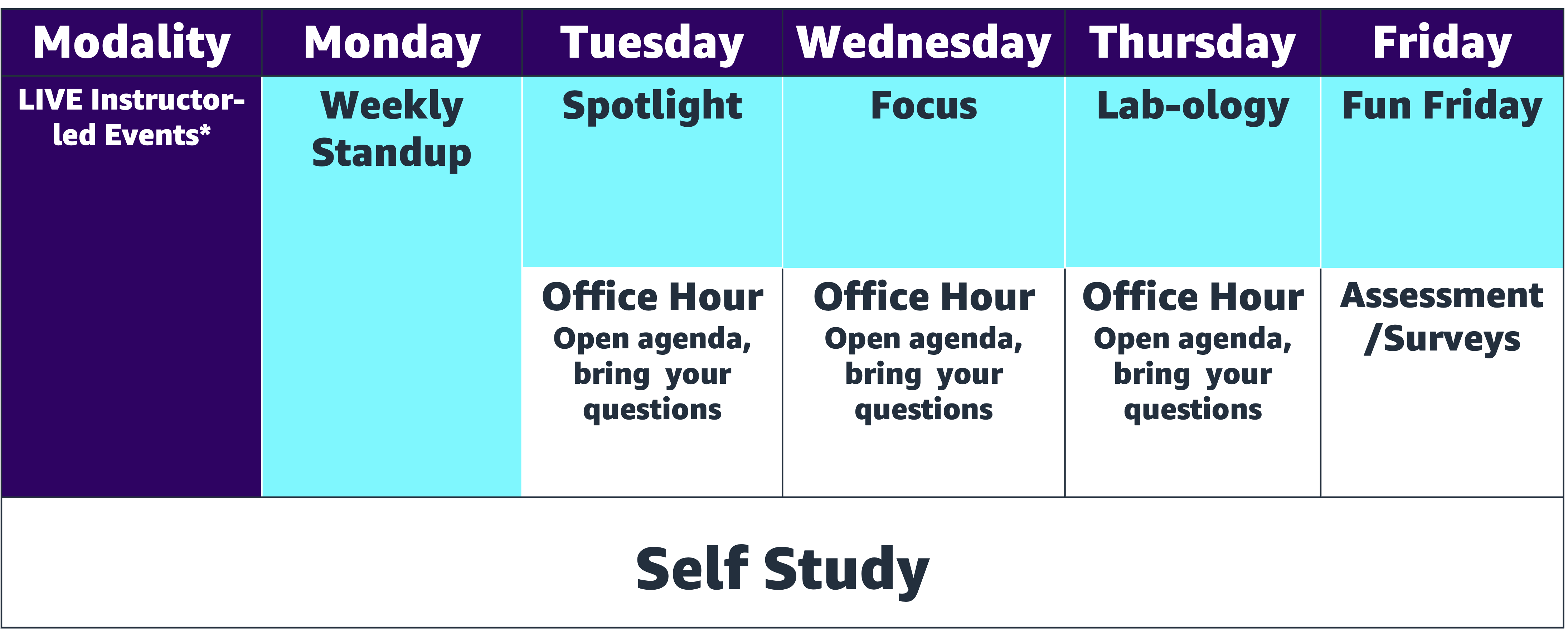
Weekly Schedule
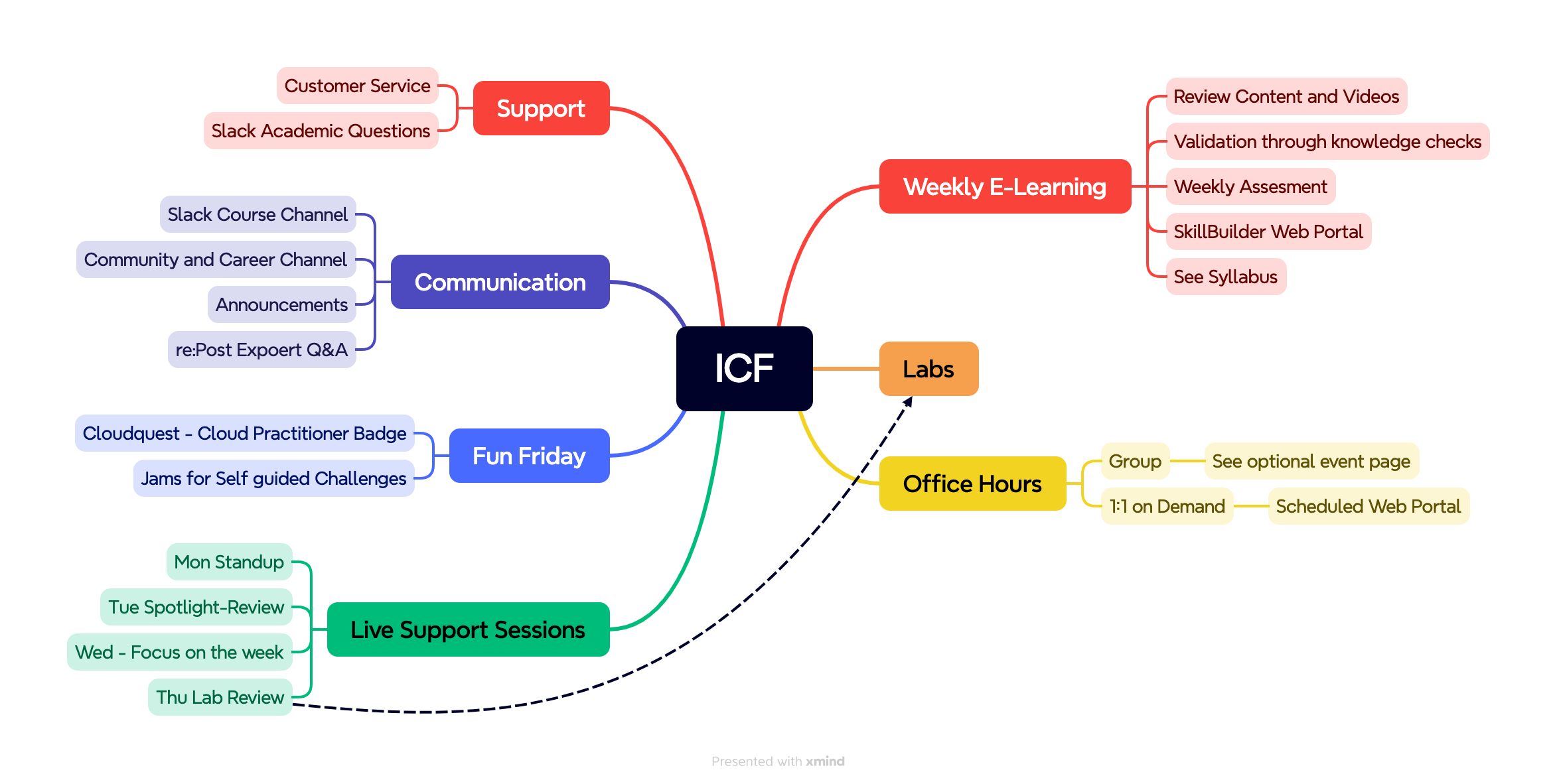
Learner Overview of ICF
Week 1
Quick Start Guide - https://explore.skillbuilder.aws/pages/95/quick-start-guide
Learner Handbook - https://explore.skillbuilder.aws/pages/84/learner-handbook
Important Calendar Dates - https://explore.skillbuilder.aws/pages/83/program-calendar
FAQ - https://explore.skillbuilder.aws/pages/85/faq
Getting help outside the classroom
Enrollment, Billing, Vouchers, Email Address Issues, Non Academic Issues
ACI Customer Support - https://support.aws.amazon.com/#/contacts/aws-training
Week 2
Play AWS Cloud Quest - https://cloudquest.skillbuilder.aws/
AWS Global Infrastructure - https://aws.amazon.com/about-aws/global-infrastructure/
Detail on AWS AZ's - https://docs.aws.amazon.com/whitepapers/latest/aws-fault-isolation-boundaries/availability-zones.html
AWS Outposts - https://aws.amazon.com/outposts/rack/hardware-specs/
IAM Best Practices - http://docs.aws.amazon.com/IAM/latest/UserGuide/best-practices.html
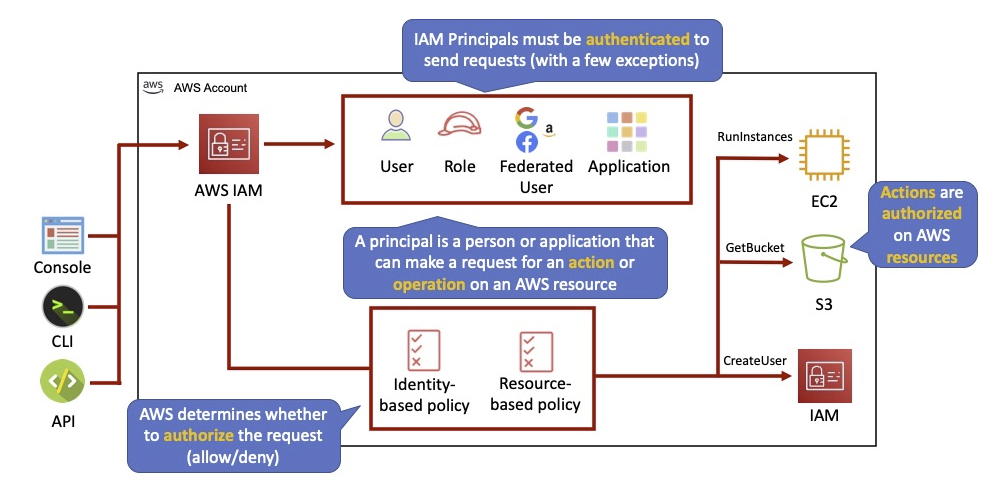
Interacting with AWS - https://docs.aws.amazon.com/whitepapers/latest/aws-overview/accessing-aws-services.html
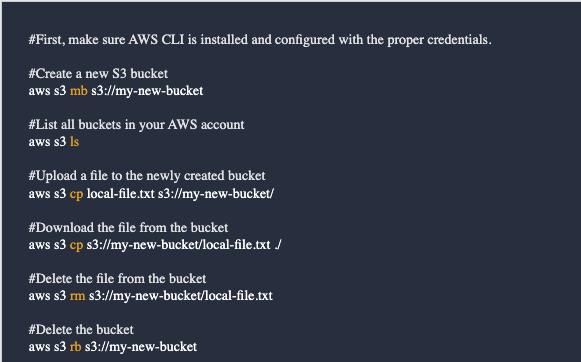
Configure the AWS CLI - https://docs.aws.amazon.com/cli/latest/userguide/cli-chap-configure.html
AWS Command Line Practice
Week 3
Learner Services
https://explore.skillbuilder.aws/pages/82/learner-services
This Thursday April 25th Cloud Chat will be posted as a video replay by 5pm ET with a link to watch.
Design Principles
Marc Petricciani, Sr. Design Architect | CS Fixed
April 25, 2024
Get to know the design principles applied in resume creation.
Assuming an IAM role using AWS CLI
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-uogKFE1r60
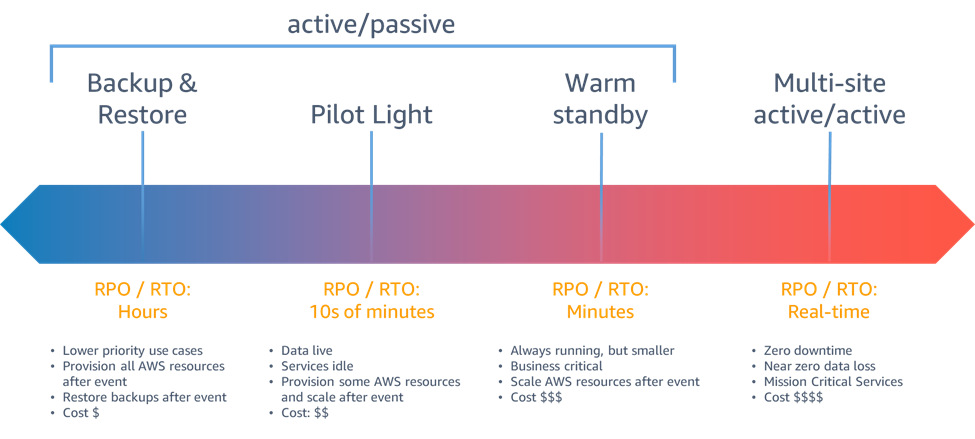
Disaster Recovery Options
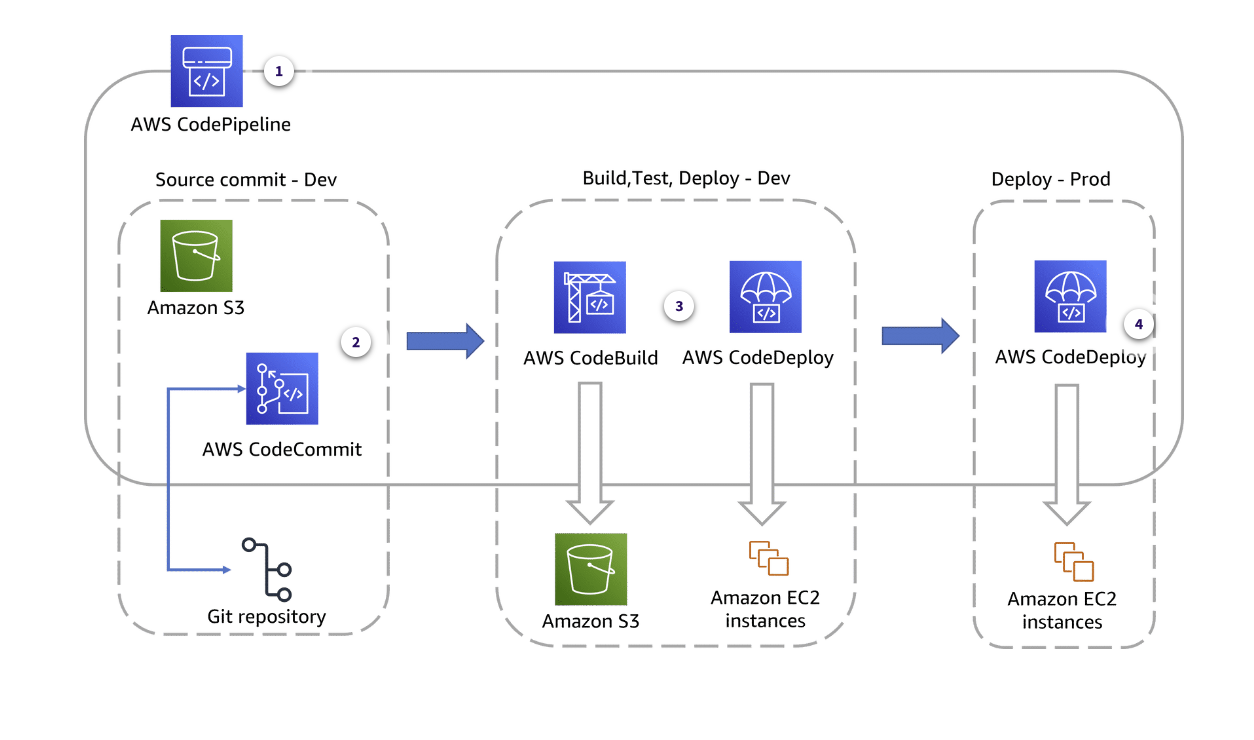
Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (CI/CD)
Lab 2 - Using Trusted Advisor
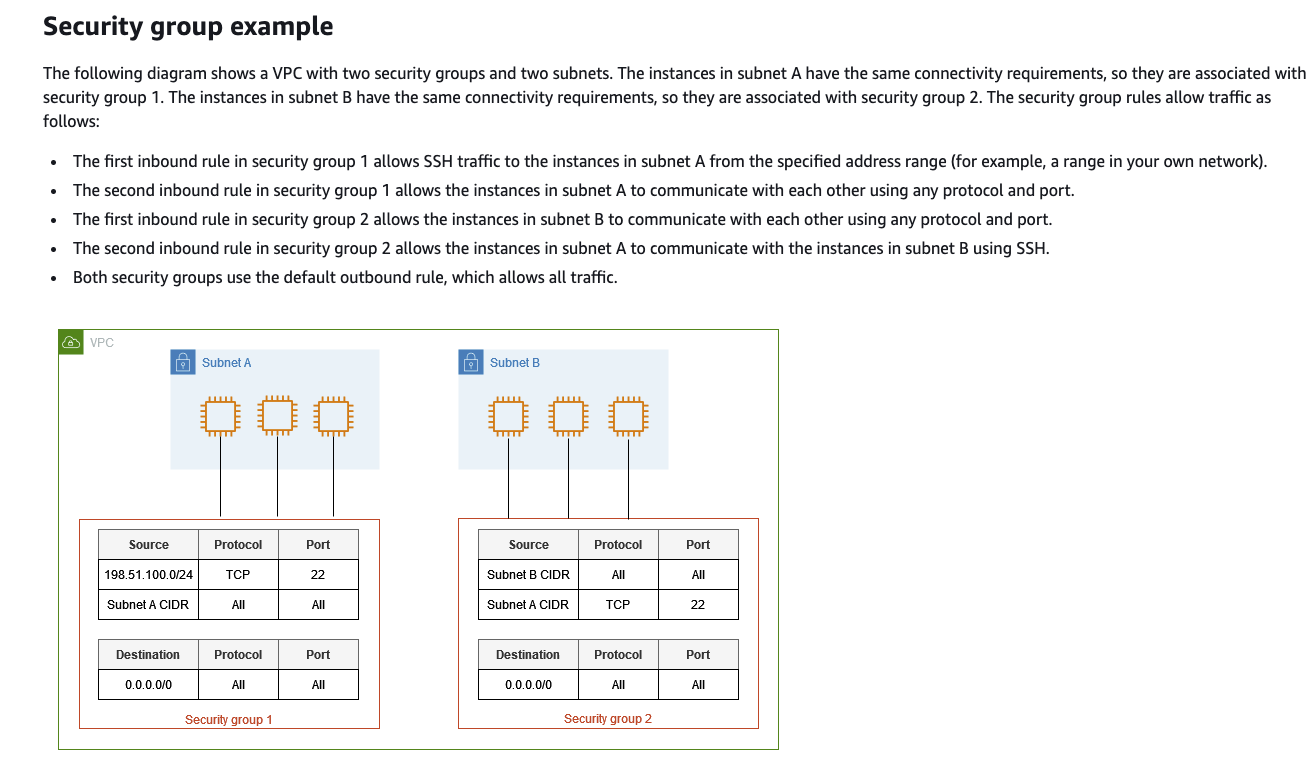
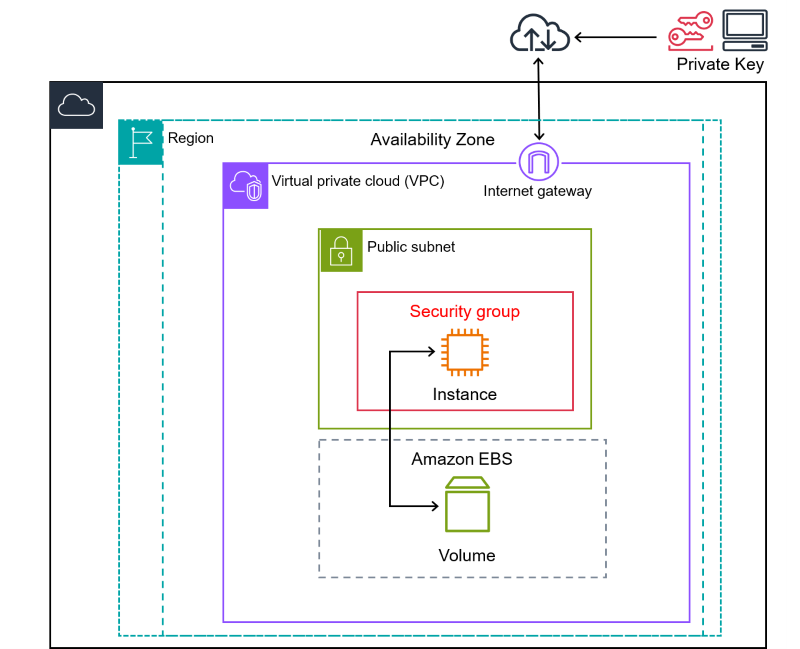
This lab practices the use of Trusted Advisor to review some security findings, one of those findings alerts the user to the fact that some unnecessary ports are exposed and how to fix them.
Security groups are logical firewalls, we will spend more time in the coming weeks showing greater depth on this subject.
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/vpc/latest/userguide/vpc-security-groups.html
Week 4 Compute
Why go from Physical Servers to Virtual Machines ?
| Physical Server | Virtual Machine |
|---|---|
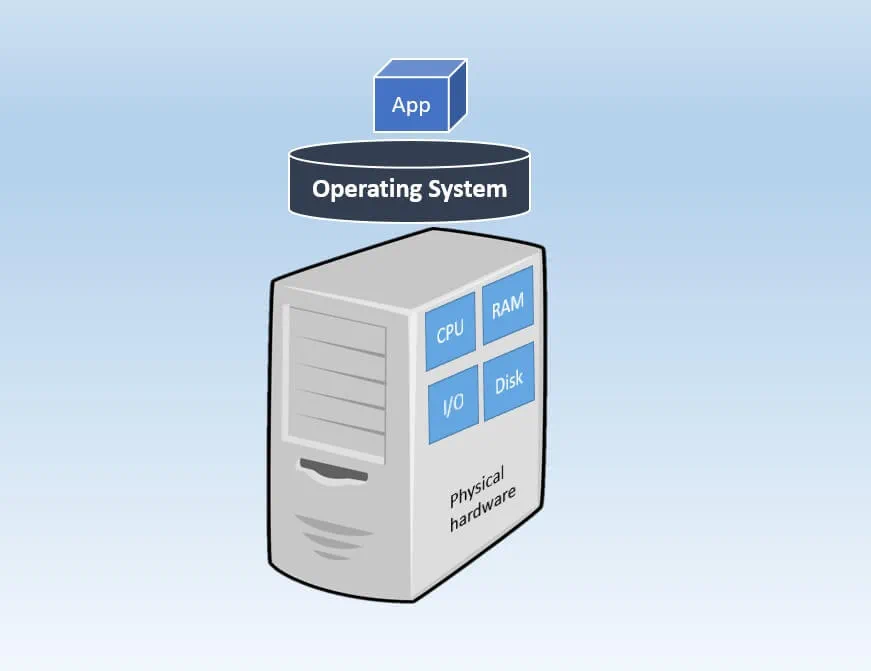 | 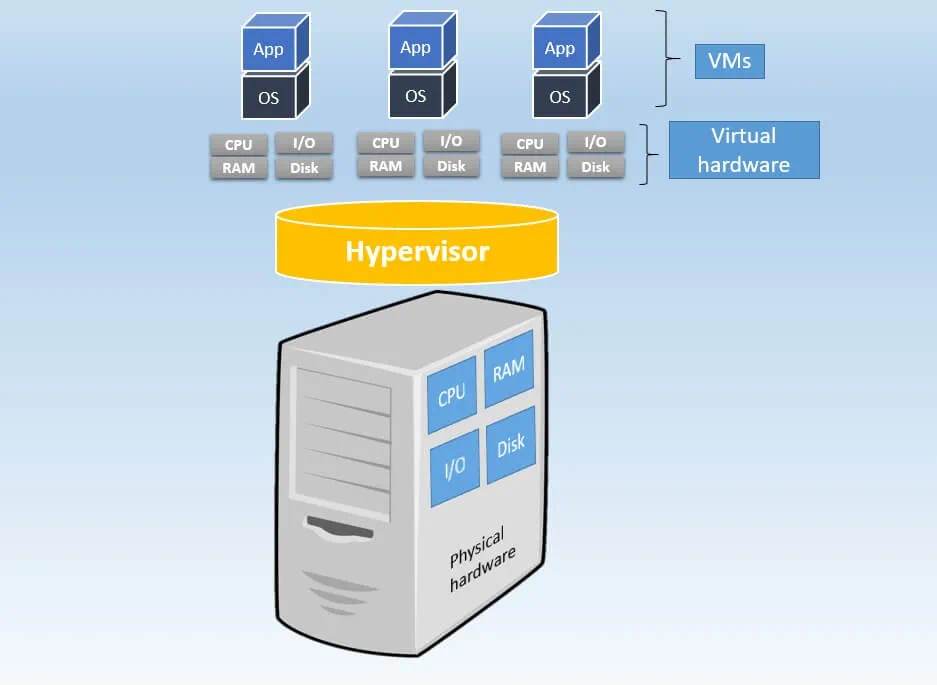 |
| Large upfront costs | Small upfront costs |
| No need for licensing purchase | VM software licenses |
| Physical servers and additional equipment take a lot of space | A single physical server can host multiple VMs, thus saving space |
| Has a short life-cycle | Supports legacy applications |
| No on-demand scalability | On-demand scalability |
| Hardware upgrades are difficult to implement and can lead to considerable downtime | Hardware upgrades are easier to implement; the workload can be migrated to a backup site for the repair period to minimize downtime |
| Difficult to move or copy | Easy to move or copy |
| Poor capacity optimization | Advanced capacity optimization is enabled by load balancing |
EC2 Instances Types Table - https://aws.amazon.com/ec2/instance-types/#instance-type-matrix
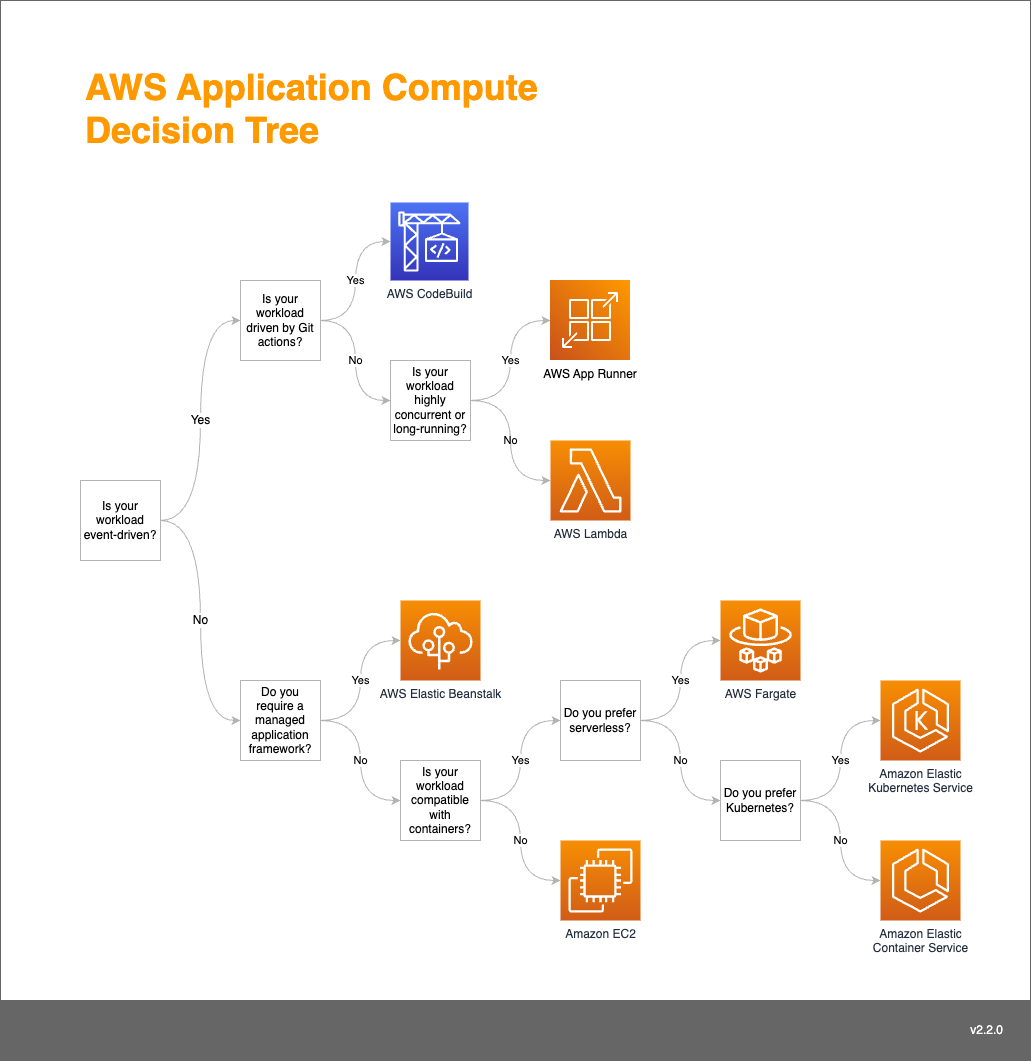
How to Choose the right Compute Platform
AWS Article - https://docs.aws.amazon.com/wellarchitected/latest/framework/perf_compute_hardware_select_best_compute_options.html
Typical EC2 Getting Started
AWS Documentation Your Friend
AWS Article User Data Scripts
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSEC2/latest/UserGuide/user-data.html
Week 4 Lab Launching an EC2 Instance using the Console
Staring Lab takes about 5 mins to warm up, Lab can take 90 mins or so to complete
Lab Tasks
Task 1: AWS Console login and Amazon EC2 console overview - (basic navigation of EC2 services page)
Task 2: Configure, launch and review the lifecycle of an EC2 instance - (launch instance, review instance state, STOP it)
Task 3: Modify an EC2 instance (modify instance t.3 micro and increase storage to gp3 - 30GB then terminate instance)
Task 4: Launch an EC2 Instance with additional configuration and test User-data implementation (check success Apache)
Task 5: Explore Reboot and Hibernate instance states - ( reboot may take a few minutes - refresh browser possible)
Task 6: Explore Elastic IP (create and associate Elastic IP - test to make sure it’s working - trouble shooting)
Task 7: Access and Explore the EC2 Instance Virtual Machine (connect and do admin update using CLI)
Task 8: Test Termination Protection
Week 5 Databases
Why go from to storing data in flat files to Databases ?
Databases were invented to provide an efficient and organized way to store, manage, and retrieve large amounts of data. Here are some of the main reasons that led to the development of database systems:
-
Data Redundancy and Inconsistency: Before databases, data was typically stored in flat files or spreadsheets, which often led to redundant and inconsistent data across different files or applications. Databases solved this problem by providing a centralized repository for data, eliminating redundancy and ensuring data consistency.
-
Data Integrity: Databases offer mechanisms to enforce data integrity rules, such as constraints and transactions, ensuring that data remains accurate and reliable even in the face of concurrent access or system failures.
-
Data Security: Databases provide built-in security features, such as user authentication, access control, and data encryption, to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access or modification.
-
Data Sharing and Concurrent Access: Databases enable multiple users or applications to access and manipulate data concurrently, while maintaining data integrity and consistency.
-
Data Independence: Databases separate the logical view of data from its physical storage, allowing changes to be made to the physical storage without affecting the logical structure or applications that access the data.
-
Query and Reporting: Databases offer powerful query languages, such as SQL, that allow users to retrieve, filter, and analyze data efficiently, enabling complex reporting and decision-making processes.
-
Application Development: Databases provide a structured and standardized way to store and access data, simplifying the development of applications that require data management capabilities.
-
Scalability and Performance: Modern database systems are designed to handle large volumes of data and provide efficient storage, indexing, and retrieval mechanisms, ensuring scalability and high performance as data grows.
The invention of databases revolutionized the way data is managed and processed, enabling organizations to leverage their data assets more effectively and make better-informed decisions.
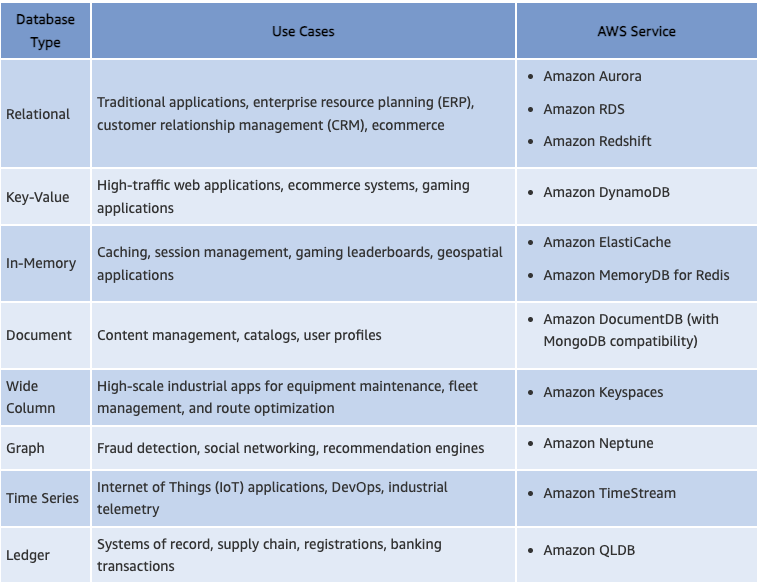
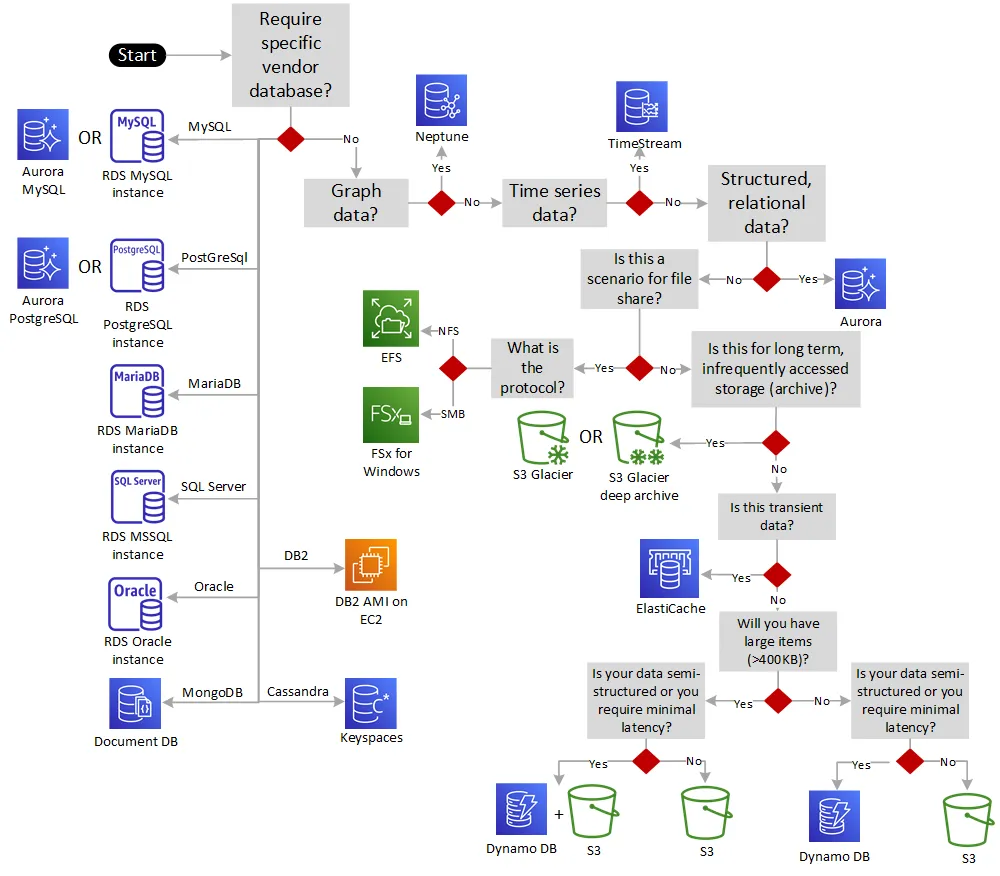
Selecting the right database and database migration plan for your workloads
Decision Tree for AWS Databases
DynamoDB
Amazon DynamoDB is a fully managed NoSQL database service that provides fast and predictable performance with seamless scalability. DynamoDB lets you offload the administrative burdens of operating and scaling a distributed database so that you don't have to worry about hardware provisioning, setup and configuration, replication, software patching, or cluster scaling. DynamoDB also offers encryption at rest, which eliminates the operational burden and complexity involved in protecting sensitive data.
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/amazondynamodb/latest/developerguide/GettingStartedDynamoDB.html
Week 6 Cloud Cost Management
Prompt to AWS Party Rock LLM
I am a new cloud application developer, learning to code on AWS cloud, what is the best way for me to help save money while I use AWS cloud services?
AWS Blog - AWS Cloud Financial Management
AWS (Amazon Web Services) places a significant emphasis on cost optimization for several reasons:
Cloud computing costs: One of the primary benefits of cloud computing is its pay-as-you-go pricing model, which allows customers to pay only for the resources they consume. However, if not managed properly, cloud costs can quickly escalate, especially for large-scale deployments or workloads with fluctuating resource demands.
Customer satisfaction: Cost optimization is crucial for customer satisfaction. By helping customers optimize their cloud spending, AWS ensures that customers can maximize the value they derive from their cloud investments, leading to higher customer retention and loyalty.
Competitive advantage: In the highly competitive cloud computing market, cost optimization can be a differentiating factor. AWS aims to provide cost-effective solutions that enable customers to achieve their business goals while minimizing unnecessary expenses.
Scalability and flexibility: AWS offers a wide range of services and pricing models, allowing customers to scale their resources up or down based on their needs. Cost optimization helps customers take advantage of this flexibility by identifying the most cost-effective configurations for their workloads.
Sustainability and efficiency: Cost optimization often goes hand-in-hand with resource optimization and efficiency. By optimizing costs, customers can reduce waste, improve resource utilization, and contribute to sustainability efforts.
Continuous improvement: AWS continuously invests in developing new cost optimization tools, features, and best practices. This ongoing effort reflects AWS's commitment to helping customers achieve cost-effective and efficient cloud deployments.
By emphasizing cost optimization, AWS aims to provide customers with a cost-effective and scalable cloud platform, enabling them to focus on their core business objectives while minimizing unnecessary expenses. This approach aligns with AWS's goal of delivering value to customers and maintaining a competitive edge in the cloud computing market.
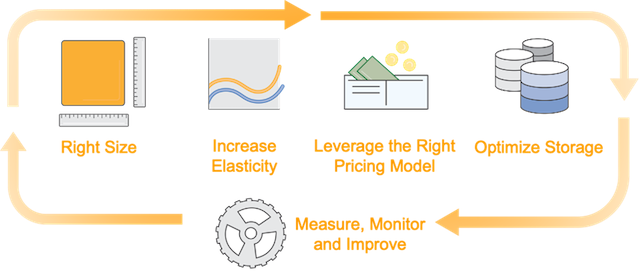
Here are some simple ways to save money on AWS services:
-
Right-sizing instances: Regularly review your instance types and sizes to ensure they match your workload requirements. Downsizing instances when possible or using Auto Scaling can help reduce costs.
-
Leverage spot instances: Spot instances are unused EC2 instances that AWS offers at a significant discount compared to On-Demand instances. They are suitable for fault-tolerant, flexible workloads.
-
Use reserved instances: For workloads with steady-state or predictable usage, reserved instances can provide significant cost savings compared to On-Demand pricing.
-
Implement auto-scaling: Auto Scaling helps automatically adjust resources based on demand, ensuring you don't pay for underutilized resources.
-
Delete unused resources: Regularly identify and remove unused or idle resources, such as unattached EBS volumes, unused Elastic IPs, or idle EC2 instances.
-
Leverage AWS pricing models: Explore different pricing models like AWS Savings Plans, which can provide discounts for consistent usage over a 1 or 3-year term.
-
Optimize storage: Use appropriate storage classes (S3 Standard, S3 Infrequent Access, or S3 Glacier) based on access patterns, and enable lifecycle policies to automatically transition objects to lower-cost tiers.
-
Implement cost monitoring and alerting: Use AWS Cost Explorer, AWS Budgets, and AWS Cost Anomaly Detection to monitor and receive alerts on unexpected cost spikes.
-
Take advantage of AWS free tier: Leverage the AWS Free Tier for eligible services to experiment and test workloads without incurring charges.
-
Consider AWS Graviton instances: AWS Graviton instances, powered by Arm-based AWS Graviton processors, can provide cost savings for certain workloads compared to x86-based instances.
By implementing these cost optimization strategies, you can significantly reduce your AWS spending while still benefiting from the scalability and flexibility of the cloud.
What is best way to setup my personal aws account to watch spending
To effectively monitor and manage spending on your personal AWS account, follow these best practices:
-
Enable AWS Cost Explorer:
- AWS Cost Explorer is a powerful tool that provides detailed insights into your AWS costs and usage.
- It allows you to visualize and analyze your costs by service, linked account, AWS Region, and more.
- Enable Cost Explorer and familiarize yourself with its features to gain visibility into your spending patterns.
-
Set up AWS Budgets:
- AWS Budgets allow you to create custom budgets and receive alerts when your actual or forecasted costs exceed the budgeted amount.
- Set up budgets based on your expected monthly or yearly spending limits.
- Configure alerts to be sent via email or Amazon Simple Notification Service (SNS) when thresholds are breached.
-
Activate AWS Cost Anomaly Detection:
- This service continuously monitors your cost and usage data to identify anomalies and potential cost spikes.
- It can alert you when it detects unusual spending patterns, helping you quickly investigate and take action.
-
Enable AWS Cost Allocation Tags:
- Cost Allocation Tags allow you to categorize and track your AWS costs based on custom tags (e.g., project, environment, department).
- Apply tags consistently across your resources to gain better visibility into cost attribution.
-
Leverage AWS Free Tier:
- AWS Free Tier offers a range of services and resources that are free for 12 months (subject to certain limits).
- Take advantage of the Free Tier for eligible services to minimize costs while experimenting or running small workloads.
-
Review AWS Trusted Advisor:
- AWS Trusted Advisor provides recommendations and best practices across various categories, including cost optimization.
- Review the cost optimization recommendations and implement the suggested actions to optimize your spending.
-
Automate Resource Cleanup:
- Implement automated processes or scripts to identify and terminate unused or idle resources (e.g., EC2 instances, EBS volumes, Elastic IPs).
- Consider using AWS Lambda functions or AWS Systems Manager Automation to automate resource cleanup.
-
Monitor AWS Billing and Cost Management Blog:
- Stay updated with the latest cost optimization tips, best practices, and new AWS cost management features by following the AWS Billing and Cost Management Blog.
By following these best practices, you can gain better visibility into your AWS spending, set appropriate budgets and alerts, and implement cost optimization strategies to effectively manage your personal AWS account costs.
관련 콘텐츠
 AWS 공식업데이트됨 2년 전
AWS 공식업데이트됨 2년 전